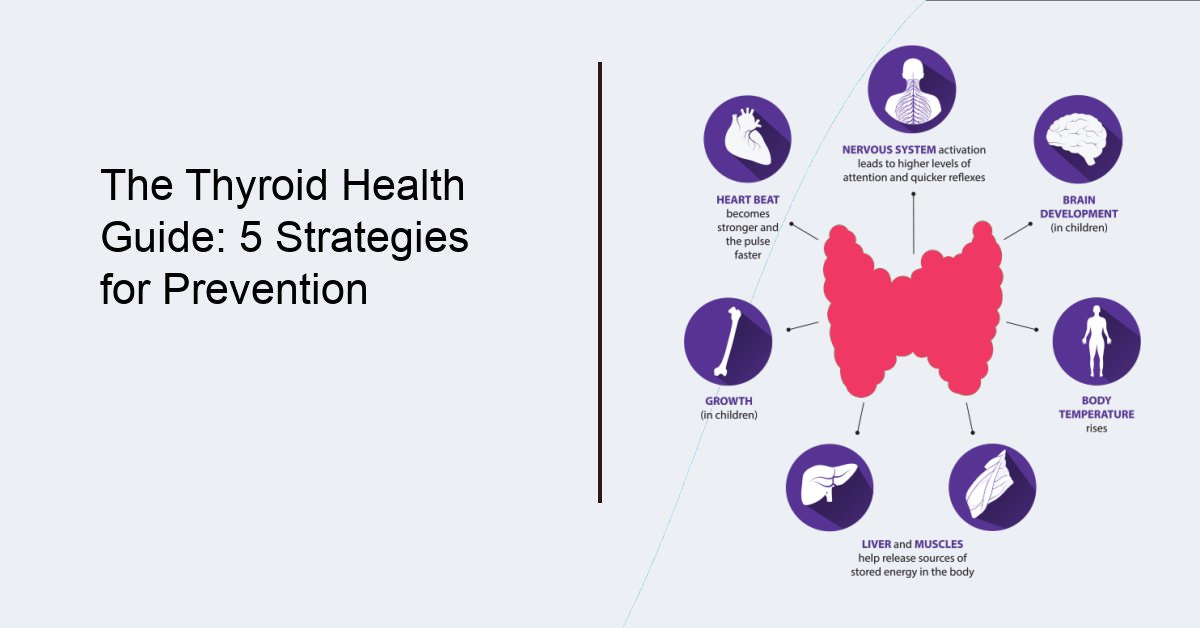
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels in the body. When the thyroid gland produces too much or too little of these hormones, it can lead to various health problems. Thyroid disorders are more common in women than men, and the risk increases with age. However, there are several thyroid prevention strategies that can be implemented to maintain a healthy thyroid gland.
In this article, you will learn five thyroid prevention strategies, the symptoms of thyroid disorders, the best diet plans, and other important considerations.
What is Thyroid?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It is an essential part of the endocrine system, which is responsible for producing and regulating hormones in the body. The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid gland is also responsible for producing calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the body. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including thyroid disorders [1].
What are Thyroid Hormones?
Thyroid hormones are hormones produced by the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. The two main thyroid hormones are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development in the body.
T4 is the most abundant thyroid hormone and is often considered the “storage” form of thyroid hormone because it is converted to T3, the more active form of the hormone, in the liver and other tissues. T3 is considered the “active” form of thyroid hormone because it is responsible for the majority of the metabolic effects of thyroid hormone in the body.
Thyroid hormones are involved in a wide range of processes in the body, including:
- Regulating metabolism and energy production
- Supporting growth and development
- Regulating body temperature
- Maintaining heart rate and blood pressure
- Regulating the digestive system
- Supporting bone health and calcium balance
When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly and producing too much or too little thyroid hormone, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including thyroid disorders.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can have various symptoms, and they depend on the type and severity of the condition. Thyroid diseases are characterized by hyperfunction (hyperthyroidism), hypofunction (hypothyoidism) or inflammation (thyroiditis) of the thyroid gland or the presence of thyroid nodules [2]. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weight changes
- Hair loss
- Sensitivity to cold or heat
- Changes in heart rate
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Muscle weakness or tremors
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering
- Depression or anxiety
- Menstrual irregularities
Thyroid dysfunction has been also associated with both female infertility, early pregnancy loss, late-pregnancy adverse events, and offspring (neuro)development [3]. There is a known link between thyroid health and diabetes, as both conditions can affect each other and have similar risk factors. Thyroid hormones play a role in regulating glucose metabolism in the body, and imbalances in thyroid function can contribute to the development of diabetes.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Five Thyroid Prevention Strategies
Get Regular Thyroid Check-Ups
Regular thyroid check-ups can help detect any abnormalities early on, which can prevent the progression of thyroid disorders. It is recommended that individuals over the age of 35 get their thyroid levels checked every five years. If you have a family history of thyroid disorders or other risk factors, such as autoimmune conditions or radiation exposure, you may need to get your thyroid levels checked more frequently.
Manage Stress
Stress can have a negative impact on thyroid health, as it can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones. It is important to implement stress-management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, to reduce stress levels. Getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and practicing self-care can also help manage stress.
Avoid Goitrogens
Goitrogens are substances that can interfere with thyroid function by blocking the uptake of iodine, which is necessary for thyroid hormone production. Some common goitrogenic foods include cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage, as well as soy products and millet. While these foods can still be consumed in moderation, it is important to avoid consuming large amounts of goitrogenic foods.
Consume Iodine-Rich Foods
Iodine is a mineral that is essential for thyroid hormone production. Consuming iodine-rich foods, such as seafood, seaweed, and iodized salt, can help support thyroid health. However, it is important not to consume excessive amounts of iodine, as this can also negatively impact thyroid function.
Follow a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help support overall health, including thyroid health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal thyroid function. Additionally, avoiding processed and sugary foods can also be beneficial for thyroid health.
Best Diet Plans for Thyroid Health
There is no specific diet plan that is guaranteed to prevent thyroid disorders, but following a healthy and balanced diet can be beneficial for thyroid health. Some foods that are particularly beneficial for thyroid health include:
Seafood
Seafood, such as fish and shellfish, is a good source of iodine, which is necessary for thyroid hormone production. Additionally, seafood is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds, such as Brazil nuts, pumpkin seeds, and chia seeds, are good sources of selenium, which is important for thyroid health. Additionally, nuts and seeds are also rich in healthy fats, fiber, and other nutrients that can support overall health.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are important sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and support thyroid health. Some fruits and vegetables that are particularly beneficial for thyroid health include:
- Berries: Berries are rich in antioxidants, which can help protect the thyroid gland from damage caused by free radicals.
- Leafy Greens: Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are rich in iron, which is necessary for thyroid hormone production.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: While cruciferous vegetables contain goitrogens, they are also rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which can support overall health. Cooking these vegetables can also help reduce their goitrogenic effects.
Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, are rich in fiber, which can help support healthy digestion and prevent constipation, a common symptom of thyroid disorders. Additionally, whole grains are also rich in B vitamins, which can support energy production and overall health.
Other Considerations for Thyroid Health
In addition to the prevention strategies and diet plans mentioned above, there are other important considerations for maintaining a healthy thyroid gland:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of thyroid disorders, as well as other health problems. Quitting smoking can help reduce this risk.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol intake can negatively impact thyroid function, as well as overall health. Limiting alcohol intake can help reduce this risk.
- Manage Medications: Some medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can negatively impact thyroid function. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional about the potential thyroid-related side effects of any medications you are taking.
Modern Research on Thyroid Health
There is ongoing research into thyroid health and thyroid disorders, as well as potential treatments and prevention strategies. Some recent studies and findings related to thyroid health include:
- Environmental Factors: A study published in the journal Nature Communications in 2021 found that exposure to common environmental chemicals, such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), can interfere with thyroid hormone signaling and increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
- Gut Microbiome: Research has shown that the gut microbiome may play a role in thyroid health. A study published in the journal Scientific Reports in 2021 found that changes in the gut microbiome were associated with thyroid function in women with hypothyroidism.
- Vitamin D: Some research has suggested that vitamin D may play a role in thyroid health. A study published in the journal Thyroid in 2020 found that vitamin D supplementation improved thyroid function in women with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Exercise: Regular exercise has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including for thyroid health. A study published in the journal BMC Endocrine Disorders in 2021 found that exercise improved thyroid function and reduced inflammation in women with subclinical hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Cancer: Thyroid cancer rates have been increasing in recent years, leading to ongoing research into potential causes and treatments. A study published in the journal Cancer in 2021 found that exposure to high levels of fine particulate air pollution may increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
These are just a few examples of the ongoing research related to thyroid health and thyroid disorders. As with any health concern, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for guidance on prevention, treatment, and management of thyroid-related issues.
Summary
Maintaining a healthy thyroid gland is important for overall health and wellbeing. By implementing the prevention strategies mentioned in this article, following a balanced diet, and considering other important factors, individuals can support their thyroid health and reduce the risk of thyroid disorders. If you experience any symptoms of thyroid disorders, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
References:
- Barrett JR, Vélez MP, Martinez A, et al. Environmental exposure to common chemicals and thyroid function among U.S. adults: A cross-sectional study. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2564. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22713-7
- Talukdar R, Saha S, Nath S, et al. Alteration of gut microbiome in hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: a comparative study. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):9621. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88864-4
- Toulis KA, Anastasilakis AD, Tzellos TG, et al. Vitamin D supplementation and thyroid function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid. 2020;30(3):389-402. doi:10.1089/thy.2019.0325
- Zhang T, Wang Y, Bai Y, et al. Effects of exercise on thyroid function in women with subclinical hypothyroidism: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021;21(1):17. doi:10.1186/s12902-020-00648-1
- Yin P, Shi X, Meng T, et al. Association between ambient fine particulate air pollution and thyroid cancer incidence: A nationwide cohort study in China. Cancer. 2021;127(3):389-398. doi:10.1002/cncr.33185.